In Star Trek The Next Generation S3 E1, the character Data is possessed by nanites who had unintentionally caused threat to the Star Fleet and in turn were attacked. By the end of the clip shown the nanites and Star Fleet have come to the agreement to stop all aggressive behavior with each other and the nanites get their own planet to inhabit.
Nanites in Terminator Genisys and Terminator 2: Judgment Day
In Terminator Genisys, the newer models use nanotechnology to shapeshift, dematerialize, and infect and control other terminators. In Terminator 2:Judgment Day, the terminators use nanotechnology to shapeshift and blend in.
Nanotech in G-Force (Disney)
Nanotechnology is used to make the tiny spy-gear and other machines that the G-force (and the villain) uses in the movie.
Options for nanotech
~I added pictures and also accidentally posted this as a draft in the beginning of the project instead of publishing it~
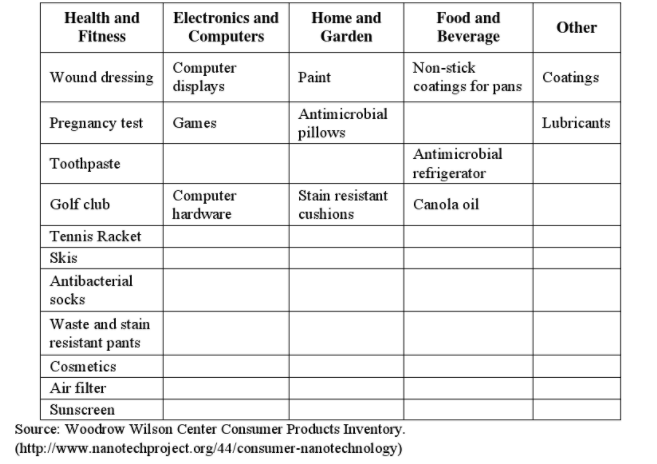
Nanotechnology covers a huge variety of items from strengthened textiles to computer parts to medicines. Nanotechnology’s use in the textile industry is usually to make cloths antibacterial, stretchier, water resistant or stronger. In computers it is used to increase resolution, memory, and processing power. In medicine it is used in wound dressings, toothpastes, cosmetics, sunscreen, medicine delivery, and illness detection.


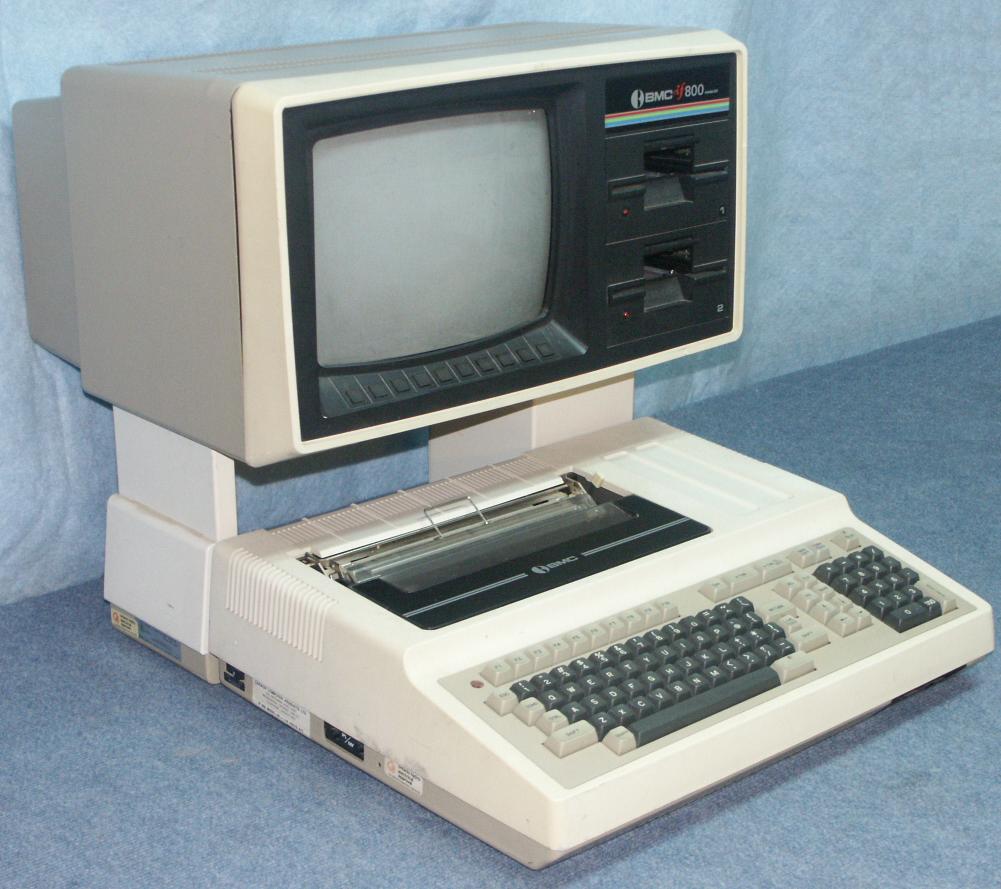
Some old computer pictures (second one is the ones that took an entire room)



A new source!
Neumann, Robert V. Nanotechnology and the environment. Nova Science Publishers, 2010, ntserver1.wsulibs.wsu.edu:3447/lib/wsu/reader.action?docID=3017727.
I am utilizing Chapters 2-4 of the book Nanotechnology and the Environment. The book assesses the benefits and potential drawbacks of nanotechnologies use through its effects on the environment. Neumann brings up the potential benefits and uses of nanotechnology for bettering or amending what people have done to the environment in chapter 2. In chapter 3, he asses the risks of using and creating nanotechnology regularly. Finally in chapter 4, Neumann describes ways to combat the risks through the responsible development of nanotechnology.
Neumann’s book is mainly for professional use/use in research and so does not have a huge amount of appeal to the general reading population. He appeals to researchers and those interested in nanotechnology’s interactions with nature through facts provided and hinted at in the introduction.
Nanotechnology and the Environment helps me further the information I can provide about the environmental effects of nanotechnology and how it can change the damage that other older technology has dealt on the environment.
Picture This
~I decided to do some edits to this part to make it sound better~
Nanotechnology. Not something you usually think about in your everyday life. But, it is all around you. It is an integral part of the laptop you do your classwork on, the phone you text your friends and family with, and soon, the medical treatment that you might someday receive. When you replace your phone’s MicroSD card that can hold 16 GigaBytes(GB) of memory, you are handling a very delicate piece composed of nanotechnology that has become an essential part of our lives. People entrust many of their fondest memories into these tiny chips, from their favorite songs to photographs of their families and vacations. All of the data held on such a small piece of technology is only a reality because of the creation of nanotechnologies. Without nanotech’s ability to hold massive amounts of information in a small area, not only would our smart phones and laptops not exist, but the amount of data we save on them would require rooms full of computers just to hold and accessing a specific file could take hours as opposed to the milliseconds it currently takes. So go ahead, fiddle with your MicroSD card, marvel at the ease you have accessing a world of information on your phone and computer. It was not too long ago that nanotechnology made all of this possible, and there’s no telling what advancements will come in the near future.
Some edits and notes for editing
FIND A WAY TO BETTER INTEGRATE THIS INTO EITHER FIRST ¶ OR SOMEWHERE ELSE (ALSO MAKE IT AN ACTUAL SENTENCE). Nanotechnology: a technology executed on the scale of less than 100 nanometers, the goal of which is to control individual atoms and molecules, especially to create computer chips and other microscopic devices (definition from dictionary.com).
Before nanotechnology started to become a tool used in medicine, it was developed for use in machines and computers. In the medical aspect, people and their doctors relied on slow releasing, directly injected, or hormonal based drugs in order to target specific areas of the patient’s body that was being affected by whatever illness they had. With nanotechnology, doctors can target specific parts of the patient’s body to be treated without affecting another area that is functioning properly and healthy. However, nanotechnology’s use did not begin in medicine; it began in computer technology. Without the implementation of nanotechnology in computers, modern cellphones, laptops/computers, and advanced machinery would not exist.
The creation of nanochips allowed people to store and quickly access massive amounts of data in very short periods of time. Before nanotechnology was implemented into computer systems, they relied on much bulkier models that took much more time to process as well as many more supplies to make (think of the huge rooms in old movies that are full of data and processors for a single computer). Those huge machines were made of metals that were mined by either people in the United States of America, risking their lives, or adults and children in 3rd world countries. <BRING IN SOME EXAMPLES (FIND ‘EM)> Unfortunately, some companies still outsource their productions to 3rd world countries in which children make up a large part of the work force, but much of the production process for nanochips and nanobots are in factories where machines do most of the precision work and adults supervise and quality check the products throughout their production. Many of the raw materials (mostly metals) of modern and old computers and phones were harvested in poor countries in horrible conditions that put both the environment they were harvested from and those harvesting them in danger. The raw materials are then shipped to factories to be melted down and/or mixed with other materials to form the basic components of the computers/phones. The components are then shipped to a larger country (ex. Japan or the US) and cut and assembled into whatever piece of technology they were harvested to be a part of.
Nanobots, machines built on the nanoscale as well as the machines used to make nanotechnologies (dictionary.com), and other nanotechnologies are made with nanocrystalline and other nano materials. Nanocrystallines are the microscopic particles (both elements and molecules) that are used to compose nanotech. These nano materials can be a byproduct of a process, naturally made, or engineered. Developers are able to utilize natural nano materials and their unique traits to build and control the nanobots that they make.
The first models of nanotechnology were made to be solely hosts for information in larger technologies. They were modeled to be implemented into the motherboards of computers to boost the processing capabilities and information storage. Today, nanotechnology can be used in a wide variety of disciplines. In medicine, different kinds of nanotechnologies are used to deploy medicines directly. If the bots fail or break before their purpose is fulfilled then they are disposed of by the body in the same way that they would if they had functioned properly and the models are improved on by the scientists/developers to ensure that the failures will not continue to happen. The process of making and fixing nanotechnology requires specific machines that are able to have extreme precision and a lot of coding.
Cerion is one United States top manufacturers of nanotechnology, they have worked to be able to mass produce nanotechnology in factories while maintaining the controlled precision that is required for the proper formation of the tech. They manage the production of the nanoparticles that they utilize in producing different kinds of nanotechnology for their consumers. The company utilizes “bottom-up” chemical manufacturing to produce the nanomaterials needed for the industrial amounts of nanotechnology for their customers. (from Cerion’s site, cerionadvancedmaterials.com)
There are two kinds of bottom-up methods in making nanomaterials. One is called chaotic process and the other is called controlled process. In the chaotic method, particles are raised to an excited state (through either heat or electricity) before conditions are changed enough for the particles to become unstable and form the nanoparticles that are needed. Many factories prefer to use the controlled process over the chaotic process of forming nanoparticles as the chaotic process can be wasteful of the materials as the size of the products can vary greatly and they must manipulate the end products to make sure they get the nano particles that they need. The controlled process is based on precision and requires very different techniques and equipment than chaotic processes. In the controlled process the atoms and/or molecules of the needed materials are precisely moved around into a form that fits what the nanoparticle will need to be in in order for it to function properly in the nanotechnology that it will be implemented into. The controlled process can require advanced machinery such as pulse lasers and molecular beams, or it can use self-limiting growth and chemical solutions that are implemented into the nanoparticles. (AZONANO, azonano.com)
The materials needed to make nanoparticles, and further on nanotechnologies, are often metals that are harvested from mines or reserves in the soil and then mixed with other elements (often times water or hydroxide). Many nanoparticles can also be made with DNA sequencing (utilizing nucleic acids), lab work, or as byproducts of mechanical or industrial processes. Nanomaterials that are made as byproducts of other processes are referred to as “incidental” nanomaterials. Incidental nanomaterials, if caught can be used in making nanotechnology, but more often than not, they are released in gases like car exhaust and smoke and are a large contributor to air pollution. The most used kinds of nanomaterials are those that are either man-made in factories (described earlier) or made through natural occurring events such as volcanic activity, radioactive decay (when an unstable atom emits radioactive particles from its nucleus in an attempt to become stable over time), metal ore, and acid mine drainage (a process of weathering rocks by which the rocks, that are usually high in sulfide, leak very acidic liquids into the surrounding area). In regards to the harvesting of materials: if the source is in the US, then all labor laws are followed; if the source is outside of the US, then the harvesting companies may utilize unethical practices, but many companies try to keep from using materials that have been harvested under unethical conditions. The materials are harvested by workers before being sent to the factories which will use them to create the nanotechnologies that can either be used in machines or in medicine.
Though both new and old computers, phones, and medicines rely on systems like this, with nanotechnology being implemented into these systems, much less materials are needed. The nanotechnology requires a fraction of the raw materials that have needed to be harvested for older models (computers) and modes of healing (medicines) resulting in a more efficient way of utilizing the limited resources that the earth provides. Now that we are seeing the effects our previous wasteful usage of the resources (ones that people used to believe we had an infinite supply of like fossil oil, precious gems, metals, and coal) the push towards more fuel and resource efficient technology has become much larger and more widely supported.
As well as efficiency, computers have moved towards using nanotechnology over more hazardous materials for their hardware. They now use nanochips that are either made from natural carbon based or manmade metal based nanoparticles. The metal particles are used for their many innate properties. Those include the optical, mechanical, magnetic, chemical, and electrical properties. Metal based nanoparticles are the most common type of nanoparticle being implemented into biomedical practices. With these, bioengineers can create nanobots that will aid in diagnostics, drug delivery, and tissue healing in patients. Without the implementation of these particles, the healing processes that patients have to go through are long and taxing on the body.
Though it is still relatively new, advances in nanotechnology research and practices in medicine are generating a lot of diverse reactions in the public. Some people are avid supporters of nanotechnology’s use in medicine and all of the benefits it entails, while others are not as enthusiastic of this still very new kind of technology being implemented into the medical treatments they, and others might eventually be receiving. Those who support nanotechnology being used in treatments for medicine like the ways that nanobots can, and are, being utilized to help people survive circumstances that they normally would have little chance of coming out of. Nanobots can be used to bring medicines directly to the parts of the body that need to be treated, minimizing the side effects of treatments.
Nanotechnology’s use in computers and other machinery has been around for quite a while longer and has made noticeable differences in people’s lives. Nanotechnology was a gateway advancement, its creation opened the door for many advancements that eventually led to the computers, laptops, and smartphones that we see today. MAYBE FIND A BETTER PLACE FOR THIS ONE…
Long before nanotechnology came into existence, people wrote about similar concepts in science-fiction novels and shows. One of the earlier instances of this is in The Tale of Cross-eyed Lefty from Tula and the Steel Flea (1881), a folk tale-styled piece by Nikolai Leskov, where the main issue has to do with a life-sized steel flee made by the English that is worked on by Russian engineers. The engineers manage to create very tiny horseshoes engraved with the signatures of the craftsmen who worked on them. The detail work needed a “microscope that could magnify five million times” in order to be properly viewed.
Another good example of nanotechnology being a forefront in literature is the 1931 short story, Microhands, by Boris Zhitkov. In this short story a surgeon creates a pair of microscopic hands that mimic the movements of his hands in order to perform more intimate and precise surgeries. The technology crated in this story is surprisingly similar to what bioengineers are now making almost 100 years later. Currently, some forms of nanobots are being implemented into the surgical world in ways very similar to those covered in Zhitkov’s story, a main surgeon can either carry out the surgery by controlling the nanorobots via remote control/computer system or the nanorobots can carry out the surgery via programming while a surgeon supervises to make sure everything goes well.
People have also reacted to nanotechnology’s existence by incorporating it into movies and television shows. In the Star Trek universe for example, from Star Trek: The Next Generation and beyond, the Borg, an antagonistic alien species in the series, utilize nanomachines, referred to as “nanoprobes”, in order to assimilate captive individuals into their following. In the TV series Stargate SG-1(July 27, 1997 – March 13, 2007) and Stargate Atlantis (July 16, 2004 – January 9, 2009), nanotechnology was featured in the form of replicators and the Asurans as well as a “nanovirus”. The Terminator series relies pretty heavily on the idea of nanotechnology, especially in Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991) and Terminator: Genesis (2015) which both feature the T-1000 model terminator that utilizes nanotechnology to give it shapeshifting abilities. The T-X model in Terminator: Rise of the Machines (2003), like T-1000 uses nanotechnology to shapeshift, but also uses it to infect and control other Terminator robots.
Since the beginning of technology, people have feared what possibilities might arise with it. Some of those fears are reflected in the media (it being used as a weapon like in Star Trek and Terminator) while others take form of “urban legends” and such through society, and recently the internet. A very popular urban legend that surfaced years ago about nanotechnology was that the United States government was creating spy drones that resembled mosquitoes “to take a DNA sample or leave RFID tracking nanotechnology on your skin” in urban areas to monitor the population. The believers of this claim also insisted that it was already in production and released. One of the inspirations for this claim was the micro air vehicles (MAVs) that the military was working on. The MAVs were designed to grant remote controlled access to areas that could not safely be infiltrated by members of the military. Many MAVs are modeled after birds and small insects in order to attain flight capabilities that they would not otherwise be able to remain airborne. This idea that the US government is using every new technology to spy on the citizens of America is not a nanotechnology-unique speculation, the government can, and does, monitor internet and cell phone usage, but not to the point where some paranoid, and even some not paranoid, people seem to believe that they do.
The actualities of nanotechnology are not very close to the weaponized uses that the public and popular media seem to think up. They are much more like the uses in the short story and folk tale that I described earlier. In computers and phones, nanotechnology is used as chips in the hardware so the devices are able to quickly and efficiently access and manipulate massive amounts of data. In order to access the same amount of data with technology that does not use nanotech, one would need the huge computers which processors took up entire rooms and took a lot longer. In medicine, nanotechnology’s use is enhancing a prolonging people’s lives. Some people fear what could happen with foreign objects (most picture tiny robots doing what they will) in their bodies, but the nanobots/particles would only stay in the system until the issue they were introduced to fix is absolved and would then be carried out with the rest of the body’s waste produces. Nanotechnologies are helping to elongate the average lifespans around the world by helping to cure people who suffer from illnesses that can often easily become terminal, like cancers by helping the body target the issue (in cancer’s case tumors). The bots are also able to aid in finding illness more accurately and using ultrasound, can help to locate internal injuries as well as aid in surgeries. Some of the smaller nanobots are able to target and modify mutated genes in DNA strands to correct certain illnesses. With nanobots, bioengineers can grow pieces of, and entire, organs for people to replace damaged/failing ones that otherwise could have costed the patient their lives. Before the option of growing new organs/organ parts was an option if patients needed to get an organ replaced they were placed on a waiting list for a transplant based on the urgency of their situation and would often die long before they were given an opportunity to have a transplant surgery.
Causing social and economic issues (working) and more medicines are needed. <IMPLEMENT THIS SOMEWHERE. REARANGE SOME STUFF.
First Draft: Nanotechnology and its Effect on Society
Before nanotechnology started to become a tool used in medicine, people and their doctors relied on slow releasing, directly injected, or hormonal based drugs in order to target specific areas of the patient’s body that was being affected by whatever illness they had. With nanotechnology, doctors can target specific parts of the patient’s body to be treated without affecting another area that is functioning properly and healthy. However, nanotechnologies use did not begin in medicine; it began in computer technology. Without the implementation of nanotechnology in computers, modern cellphones, laptops/computers, and advanced machinery would not exist.
The creation of nanochips allowed people to store and quickly access massive amounts of data in very short periods of time. Before nanotechnology was implemented into computer systems, they relied on much bulkier models that took much more time to process as well as many more supplies to make (think of the huge rooms in old movies that are full of data and processors for a single computer). Those huge machines were made of metals that were mined by either people in the United States of America, risking their lives, or adults and children in 3rd world countries. Unfortunately, some companies still outsource their productions to 3rd world countries in which children make up a large part of the work force, but much of the production process for nanochips and nanobots are in factories where machines do most of the precision work and adults supervise and quality check the products throughout their production. Many of the raw materials (mostly metals) of modern and old computers and phones were harvested in poor countries in horrible conditions that put both the environment they were harvested from and those harvesting them in danger. The raw materials are then shipped to factories to be melted down and/or mixed with other materials to form the basic components of the computers/phones. The components are then shipped to a larger country (ex. Japan or the US) and cut and assembled into whatever piece of technology they are needed in.
Nanobots and other nanotechnologies are made with nanocrystalline and other nano materials. These nano materials can be a byproduct of a process, naturally made, or engineered. Developers are able to utilize natural nano materials and their unique traits to build and control the nanobots that they make. The first models of nanotechnology were made to be solely hosts for information in larger technologies. They were modeled to be implemented into the motherboards of computers to boost the processing capabilities and information storage. Today, nanotechnology can be used in a wide variety of disciplines. In medicine, different kinds of nanotechnologies are used to deploy medicines directly. If the bots fail or break before their purpose is fulfilled then they are disposed of by the body in the same way that they would if they had functioned properly and the models are improved on by the scientists/developers to ensure that the failures will not continue to happen. The process of making and fixing nanotechnology requires specific machines that are able to have extreme precision and a lot of coding.
Cerion is one United States top manufacturers of nanotechnology, they have worked to be able to mass produce nanotechnology in factories while maintaining the controlled precision that is required for the proper formation of the tech. They manage the production of the nanoparticles that they utilize in producing different kinds of nanotechnology for their consumers. The company utilizes “bottom-up” chemical manufacturing to produce the nanomaterials needed for the industrial amounts of nanotechnology for their customers.
There are two kinds of bottom-up methods in making nanomaterials. One is called chaotic process and the other is called controlled process. In the chaotic method, particles are raised to an excited state (through either heat or electricity) before conditions are changed enough for the particles to become unstable and form the nanoparticles that are needed. Many factories prefer to use the controlled process over the chaotic process of forming nanoparticles as the chaotic process can be wasteful of the materials as the size of the products can vary greatly and they must manipulate the end products to make sure they get the nano particles that they need. The controlled process is based on precision and requires very different techniques and equipment than chaotic processes. In the controlled process the atoms and/or molecules of the needed materials are precisely moved around into a form that fits what the nanoparticle will need to be in in order for it to function properly in the nanotechnology that it will be implemented into. The controlled process can require advanced machinery such as pulse lasers and molecular beams, or it can use self-limiting growth and chemical solutions that are implemented into the nanoparticles.
The materials needed to make nanoparticles, and further on nanotechnologies, are often metals that are harvested from mines or reserves in the soil and then mixed with other elements (often times water or hydroxide). Many nanoparticles can also be made with DNA sequencing (utilizing nucleic acids), lab work, or as byproducts of mechanical or industrial processes. Nanomaterials that are made as byproducts of other processes are referred to as “incidental” nanomaterials. Incidental nanomaterials, if caught can be used in making nanotechnology, but more often than not, they are released in gases like car exhaust and smoke and are a large contributor to air pollution. The most used kinds of nanomaterials are those that are either man-made in factories (described earlier) or made through natural occurring events such as volcanic activity, radioactive decay (when an unstable atom emits radioactive particles from its nucleus in an attempt to become stable over time), metal ore, and acid mine drainage (a process of weathering rocks by which the rocks, that are usually high in sulfide, leak very acidic liquids into the surrounding area). In regards to the harvesting of materials: if the source is in the US, then all labor laws are followed; if the source is outside of the US, then the harvesting companies may utilize unethical practices, but many companies try to keep from using materials that have been harvested under unethical conditions. The materials are harvested by workers before being sent to the factories which will use them to create the nanotechnologies that can either be used in machines or in medicine.
Though both new and old computers, phones, and medicines rely on systems like this, with nanotechnology being implemented into these systems, much less materials are needed. The nanotechnology requires a fraction of the raw materials that have needed to be harvested for older models (computers) and modes of healing (medicines) resulting in a more efficient way of utilizing the limited resources that the earth provides. Now that we are seeing the effects our previous wasteful usage of the resources (ones that people used to believe we had an infinite supply of like fossil oil, precious gems, metals, and coal) the push towards more fuel and resource efficient technology has become much larger and more widely supported.
As well as efficiency, computers have made a move towards much less hazardous materials being required for their hardware as well. Nanochips used in computers are either made from naturally occurring carbon based nanoparticles or manmade metal based nanoparticles. The metal nanoparticles are used because of their optical, mechanical, magnetic, chemical, and electrical properties. Metal based nanoparticles are the most common type of nanoparticle that is being implemented into biomedical practices. With these nanoparticles, bioengineers can create nanobots that will aid in diagnostics, drug delivery, and tissue healing in patients. Without the implementation of these particles, the healing processes that patients have to go through are long and taxing on the body. With the particles bioengineers can grow pieces of, and entire, organs for people to replace damaged/failing ones that otherwise could have costed the patient their lives. Before the option of growing new organs/organ parts was an option if patients needed to get an organ replaced they were placed on a waiting list for a transplant based on the urgency of their situation and would often die long before they were given an opportunity to have a transplant surgery.
Though it is still relatively new, advances in nanotechnology research and practices in medicine are generating a lot of diverse reactions in the public. Some people are avid supporters of nanotechnology’s use in medicine and all of the benefits it entails, while others are not as enthusiastic of this still very new kind of technology being implemented into the medical treatments they, and others might eventually be receiving. Those who support nanotechnology being used in treatments for medicine like the ways that nanobots can, and are, being utilized to help people survive circumstances that they normally would have little chance of coming out of. Nanobots can be used to bring medicines directly to the parts of the body that need to be treated, minimizing the side effects of treatments.
Nanotechnology’s use in computers and other machinery has been around for quite a while longer and has made noticeable differences in people’s lives. Nanotechnology was a gateway advancement, its creation opened the door for many advancements that eventually led to the computers, laptops, and smartphones that we see today.
Long before nanotechnology came into existence, people wrote about similar concepts in science-fiction novels and shows. One of the earlier instances of this is in The Tale of Cross-eyed Lefty from Tula and the Steel Flea (1881), a folk tale-styled piece by Nikolai Leskov, where the main issue has to do with a life-sized steel flee made by the English that is worked on by Russian engineers. The engineers manage to create very tiny horseshoes engraved with the signatures of the craftsmen who worked on them. The detail work needed a “microscope that could magnify five million times” in order to be properly viewed.
Another good example of nanotechnology being a forefront in literature is the 1931 short story, Microhands, by Boris Zhitkov. In this short story a surgeon creates a pair of microscopic hands that mimic the movements of his hands in order to perform more intimate and precise surgeries. The technology crated in this story is surprisingly similar to what bioengineers are now making almost 100 years later. Currently, some forms of nanobots are being implemented into the surgical world in ways very similar to those covered in Zhitkov’s story, a main surgeon can either carry out the surgery by controlling the nanorobots via remote control/computer system or the nanorobots can carry out the surgery via programming while a surgeon supervises.
People have also reacted to nanotechnology’s existence by incorporating it into movies and television shows. In the Star Trek universe for example, from Star Trek: The Next Generation and beyond, the Borg, an antagonistic alien species in the series, utilize nanomachines, referred to as “nanoprobes”, in order to assimilate captive individuals into their following. In the TV series Stargate SG-1(July 27, 1997 – March 13, 2007) and Stargate Atlantis (July 16, 2004 – January 9, 2009), nanotechnology was featured in the form of replicators and the Asurans as well as a “nanovirus”. The Terminator series relies pretty heavily on the idea of nanotechnology, especially in Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991) and Terminator: Genesis (2015) which both feature the T-1000 model terminator that utilizes nanotechnology to give it shapeshifting abilities. The T-X model in Terminator: Rise of the Machines (2003), like T-1000 uses nanotechnology to shapeshift, but also uses it to infect and control other Terminator robots.
Since the beginning of technology, people have feared what possibilities might arise with it. Some of those fears are reflected in the media (it being used as a weapon like in Star Trek and Terminator) while others take form of “urban legends” and such through society, and recently the internet. A very popular urban legend that surfaced years ago about nanotechnology was that the United States government was creating spy drones that resembled mosquitoes “to take a DNA sample or leave RFID tracking nanotechnology on your skin” in urban areas to monitor the population. The believers of this claim also insisted that it was already in production and released. One of the inspirations for this claim was the micro air vehicles (MAVs) that the military was working on. The MAVs were designed to grant remote controlled access to areas that could not safely be infiltrated by members of the military. Many MAVs are modeled after birds and small insects in order to attain flight capabilities that they would not otherwise be able to remain airborne. This idea that the US government is using every new technology to spy on the citizens of America is not a nanotechnology-unique speculation, the government can, and does, monitor internet and cell phone usage, but not to the point where some paranoid, and even some not paranoid, people seem to believe that they do.
The actualities of nanotechnology are not very close to the weaponized uses that the public and popular media seem to think up. They are much more like the uses in the short story and folk tale that I described earlier. In computers and phones, nanotechnology is used as chips in the hardware so the devices are able to quickly and efficiently access and manipulate massive amounts of data. In order to access the same amount of data with technology that does not use nanotech, one would need the huge computers which processors took up entire rooms and took a lot longer. In medicine, nanotechnology’s use is enhancing a prolonging people’s lives. Some people fear what could happen with foreign objects (most picture tiny robots doing what they will) in their bodies, but the nanobots/particles would only stay in the system until the issue they were introduced to fix is absolved and would then be carried out with the rest of the body’s waste produces. Nanotechnologies are helping to elongate the average lifespans around the world by helping to cure people who suffer from illnesses that can often easily become terminal, like cancers by helping the body target the issue (in cancer’s case tumors). The bots are also able to aid in finding illness more accurately and using ultrasound, can help to locate internal injuries as well as aid in surgeries. Some of the smaller nanobots are able to target and modify mutated genes in DNA strands to correct certain illnesses.
Nanotechnology and People’s Perceptions and the Media
Though it is still relatively new, advances in nanotechnology research and practices in medicine are generating a lot of diverse reactions in the public. Some people are avid supporters of nanotechnology’s use in medicine and all of the benefits it entails, while others are not as enthusiastic of this still very new kind of technology being implemented into the medical treatments they, and others might eventually be receiving. Those who support nanotechnology being used in treatments for medicine like the ways that nanobots can, and are, being utilized to help people survive circumstances that they normally would have little chance of coming out of. Nanobots can be used to bring medicines directly to the parts of the body that need to be treated, minimizing the side effects of treatments.
Nanotechnology’s use in computers and other machinery has been around for quite a while longer and has made noticeable differences in people’s lives. Nanotechnology was a gateway advancement, its creation opened the door for many advancements that eventually led to the computers, laptops, and smartphones that we see today.
Long before nanotechnology came into existence, people wrote about similar concepts in science-fiction novels and shows. One of the earlier instances of this is in The Tale of Cross-eyed Lefty from Tula and the Steel Flea (1881), a folk tale-styled piece by Nikolai Leskov, where the main issue has to do with a life-sized steel flee made by the English that is worked on by Russian engineers. The engineers manage to create very tiny horseshoes engraved with the signatures of the craftsmen who worked on them. The detail work needed a “microscope that could magnify five million times” in order to be properly viewed.
Another good example of nanotechnology being a forefront in literature is the 1931 short story, Microhands, by Boris Zhitkov. In this short story a surgeon creates a pair of microscopic hands that mimic the movements of his hands in order to perform more intimate and precise surgeries. The technology crated in this story is surprisingly similar to what bioengineers are now making almost 100 years later. Currently, some forms of nanobots are being implemented into the surgical world in ways very similar to those covered in Zhitkov’s story, a main surgeon can either carry out the surgery by controlling the nanorobots via remote control/computer system or the nanorobots can carry out the surgery via programming while a surgeon supervises.
People have also reacted to nanotechnology’s existence by incorporating it into movies and television shows. In the Star Trek universe for example, from Star Trek: The Next Generation and beyond, the Borg, an antagonistic alien species in the series, utilize nanomachines, referred to as “nanoprobes”, in order to assimilate captive individuals into their following. In the TV series Stargate SG-1(July 27, 1997 – March 13, 2007) and Stargate Atlantis (July 16, 2004 – January 9, 2009), nanotechnology was featured in the form of replicators and the Asurans as well as a “nanovirus”. The Terminator series relies pretty heavily on the idea of nanotechnology, especially in Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991) and Terminator: Genesis (2015) which both feature the T-1000 model terminator that utilizes nanotechnology to give it shapeshifting abilities. The T-X model in Terminator: Rise of the Machines (2003), like T-1000 uses nanotechnology to shapeshift, but also uses it to infect and control other Terminator robots.
Since the beginning of technology, people have feared what possibilities might arise with it. Some of those fears are reflected in the media (it being used as a weapon like in Star Trek and Terminator) while others take form of “urban legends” and such through society, and recently the internet. A very popular urban legend that surfaced years ago about nanotechnology was that the United States government was creating spy drones that resembled mosquitoes “to take a DNA sample or leave RFID tracking nanotechnology on your skin” in urban areas to monitor the population. The believers of this claim also insisted that it was already in production and released. One of the inspirations for this claim was the micro air vehicles (MAVs) that the military was working on. The MAVs were designed to grant remote controlled access to areas that could not safely be infiltrated by members of the military. Many MAVs are modeled after birds and small insects in order to attain flight capabilities that they would not otherwise be able to remain airborne. This idea that the US government is using every new technology to spy on the citizens of America is not a nanotechnology-unique speculation, the government can, and does, monitor internet and cell phone usage, but not to the point where some paranoid, and even some not paranoid, people seem to believe that they do.
The actualities of nanotechnology are not very close to the weaponized uses that the public and popular media seem to think up. They are much more like the uses in the short story and folk tale that I described earlier. In computers and phones, nanotechnology is used as chips in the hardware so the devices are able to quickly and efficiently access and manipulate massive amounts of data. In order to access the same amount of data with technology that does not use nanotech, one would need the huge computers which processors took up entire rooms and took a lot longer. In medicine, nanotechnology’s use is enhancing a prolonging people’s lives. Some people fear what could happen with foreign objects (most picture tiny robots doing what they will) in their bodies, but the nanobots/particles would only stay in the system until the issue they were introduced to fix is absolved and would then be carried out with the rest of the body’s waste produces. Nanotechnologies are helping to elongate the average lifespans around the world by helping to cure people who suffer from illnesses that can often easily become terminal, like cancers by helping the body target the issue (in cancer’s case tumors). The bots are also able to aid in finding illness more accurately and using ultrasound, can help to locate internal injuries as well as aid in surgeries. Some of the smaller nanobots are able to target and modify mutated genes in DNA strands to correct certain illnesses.